P R O L E A R N
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, creates objects by depositing materials layer by layer. In the realm of circular and regenerative design, it offers unprecedented opportunities for sustainability and innovation.
Cost Efficiencies
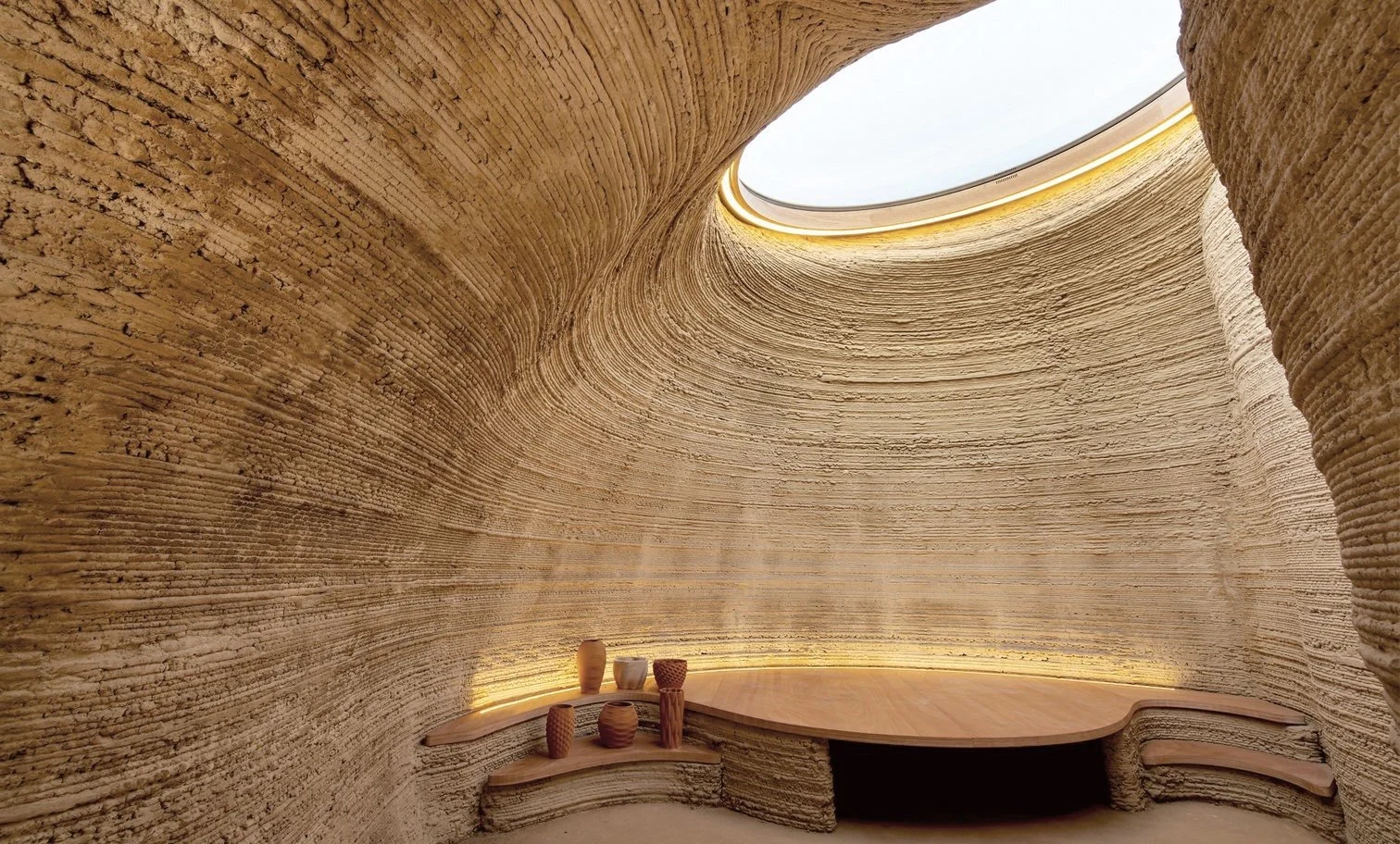
Reduced Material Waste: 3D printing significantly reduces waste compared to traditional manufacturing. For instance, Habitat for Humanity reported a 15% reduction in overall building costs per square foot using 3D printing techniques.
Lower Labour Costs: The automation in 3D printing can reduce labour costs by up to 80%, according to industry leader WinSun.
Efficient Prototyping: Rapid prototyping capabilities reduce development costs and time-to-market for new designs.
Carbon Advantages
Localised Production: By enabling on-demand, local manufacturing, 3D printing reduces transportation-related emissions and supports a more sustainable supply chain.
Energy Efficiency: 3D printing often requires less energy compared to traditional manufacturing methods. In aerospace applications, lighter 3D-printed parts lead to reduced fuel consumption and emissions.
Optimised Material Use: Advanced software allows for design optimisation, reducing material usage and associated carbon footprint.
Innovative Applications
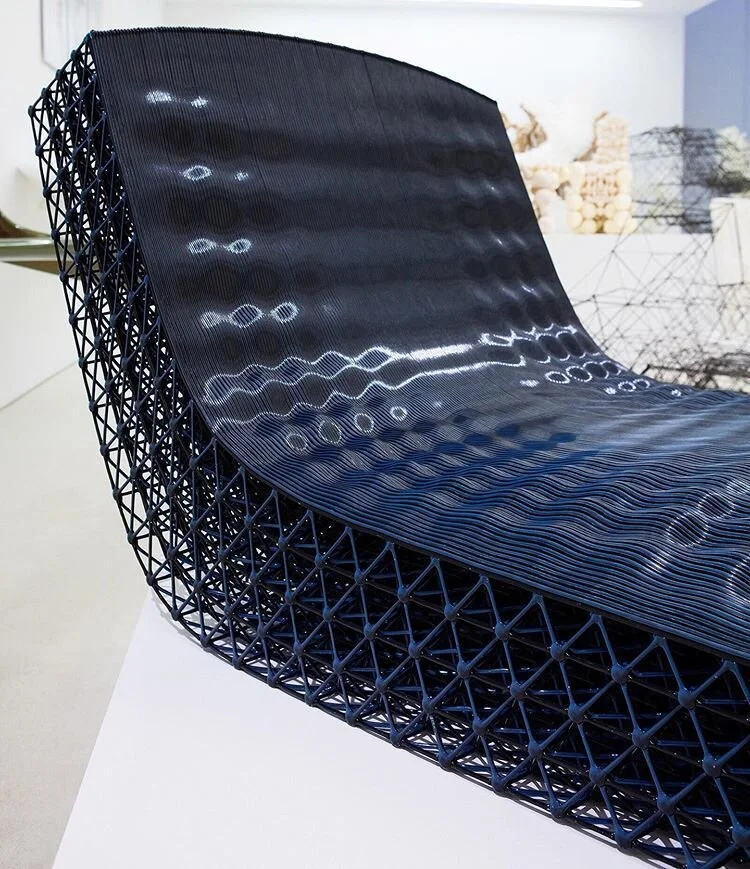
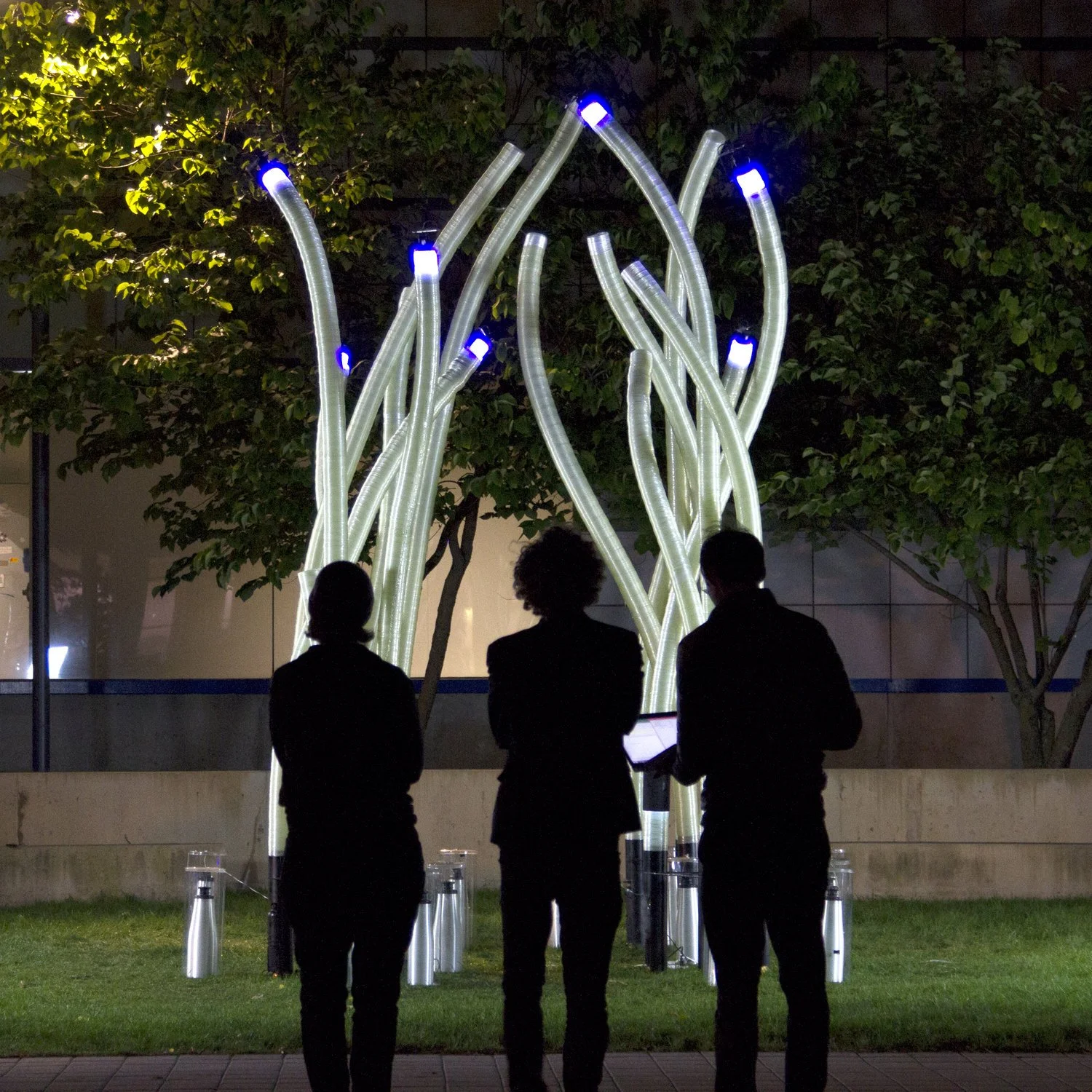
Complex Geometries: 3D printing enables the creation of intricate designs that optimise material use and improve product performance.
Sustainable Materials: The technology supports the use of biodegradable and recyclable materials, such as PLA derived from renewable resources.
Circular Economy Support: 3D printing facilitates easier product disassembly, repair, and recycling, supporting circular economy principles.
Challenges and Considerations
Initial Investment: While long-term savings are significant, the initial cost of 3D printing equipment and R&D can be high.
Material Limitations: Not all traditional construction materials are suitable for 3D printing, necessitating ongoing research and development.
Regulatory Adaptation: Building codes and regulations may need to evolve to fully accommodate 3D-printed structures.
Future Outlook
The potential for 3D printing in sustainable construction is immense. As logistical barriers are overcome and materials science advances, 3D printing is poised to play a crucial role in achieving more sustainable, circular, and regenerative built environments.
Call to Action:
Evaluate your current design and production processes to identify opportunities for integrating 3D printing. Consider pilot projects that leverage this technology's sustainability benefits, and stay informed about evolving materials and techniques in the 3D printing space.