P R O L E A R N
Reversible Design refers to the approach of creating buildings, structures, or products that can be easily disassembled, with their components reused or repurposed. This strategy aims to reduce waste, conserve resources, and enable adaptability in the built environment.
Key Principles
Modularity: Designing with standardised, interchangeable components.
Accessible Connections: Using reversible fasteners and connections for easy disassembly.
Material Selection: Choosing durable, reusable, or recyclable materials.
Documentation: Providing detailed information on assembly and disassembly processes.
Benefits
Waste Reduction: Reversible design can significantly reduce construction and demolition waste.
Resource Conservation: Enables the reuse of building components, reducing the need for new materials.
Adaptability: Allows buildings to be more easily modified for changing needs, potentially extending their lifespan.
Challenges and Considerations
Initial Costs: Reversible designs may have higher upfront costs due to specialised components and connections.
Technical Complexity: Requires careful planning and potentially new construction techniques.
Regulatory Barriers: Existing building codes may not fully accommodate reversible design principles.
Innovative Applications
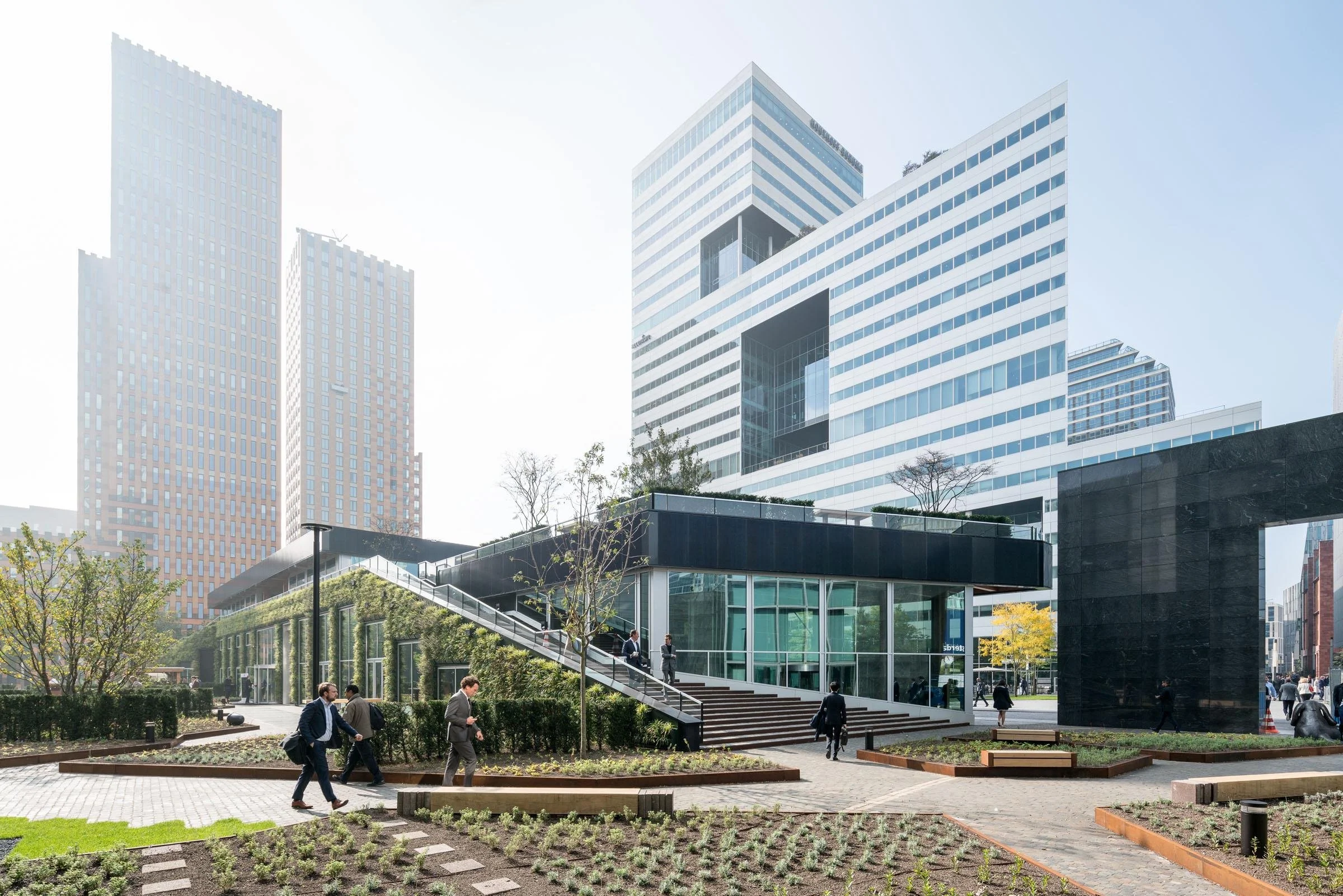
Modular Buildings: Structures like the People's Pavilion by Overtreders W and Bureau SLA, made entirely of borrowed materials.
Adaptive Reuse: Designing office buildings that can be easily converted to residential use, like some Olympic Village projects.
Product Design: Creating furniture or electronics that can be easily disassembled for repair or recycling.
Future Outlook
As sustainability becomes increasingly critical in construction, reversible design is likely to gain prominence. We can expect to see more integration of these principles in building codes and design practices, potentially leading to a more circular economy in the built environment.
Call to Action:
Evaluate your current projects for opportunities to incorporate reversible design principles. Consider how designing for disassembly could enhance the long-term value and sustainability of your buildings or products.